Asynchronous programming
Why asynchronous programming
Asynchronous programming 是個反人類的思考的東西,就算選擇不同的程式語言,共識最好的Network programming model,都是這個樣子,一個connection一個thread
1 | listen(socket_fd, 20); |
這個Model可以解決95%的問題,不過人生最難的就是那個But,這個Programming Model不能Scale
C10K Problem (1999)
這就是著名的C10K Problem,是Operation System的問題,OS不能有跟Connection一樣多的Thread,就算可以,也會耗費大量的Memory,以及頻繁的Context Switch
山不轉路轉,於是出現了IO multiplexing技術,也就是大家熟知的select/poll/epoll
The early stage of asynchronous programming
一開始的asynchronous programming,就算是libuv,asio或是nodejs等,都需要一個callback當參數,寫著寫著就會變成這樣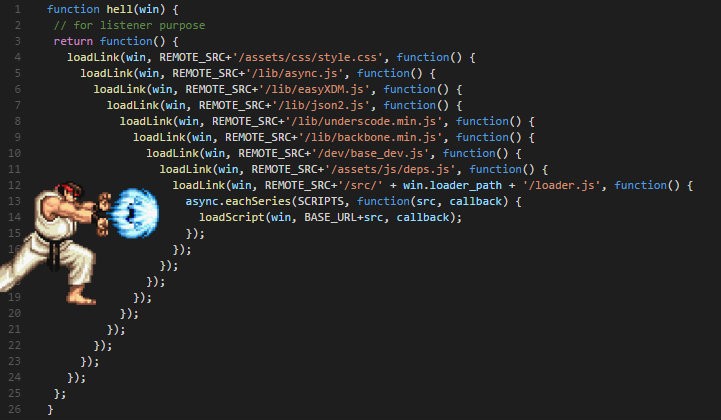
The problem of callback
- 反人類
Thread based solution之所以被推崇,就是人類的思考模式傾向於直線思考,而Callback based solution需要將步驟切得七零八落,慘不忍睹
- 難寫易錯
假設事務夠簡單,一兩層callback就能解決的話,事情還好辦,當邏輯複雜到一個程度,寫錯的機率實在是太高了
Source Code是要寫給人看的,因此需要有工具來管理複雜度,也就是Coroutine
System Language對於Coroutine的態度
- C:不關我的事,你自己想辦法
- C++: 到了2021年還沒有標準的Network Library:會不會太落後
- Rust: 比C++早訂定標準:不過押寶押錯了:標準也定了:改不了了:至於押寶押錯這件事後面再說
What is coroutine
太陽底下沒有新鮮事,Coroutine在1963年就被提出,過了五十年後重新被人想起
Coroutine擁有以下四種特性
- Invoke
- Return
- Yield
- Resume
而我們一般所知道的Function就只有
- Invoke
- Return
也就是Function只是Coroutine的特殊案例
Coroutine的另一項特性
- Cooperative multitasking
同樣的,太陽底下沒有新鮮事
聽過當初Windows 3.1常常會程式卡死,而Windows 95不會,就是因為將Cooperative multitasking改成Pre-emptive multitasking
The simplest example on coroutine
雖然這範例沒什麼用,不過能夠讓我們了解Corotuine的本質,能夠Yield和Resume
switch的case可以包含在for loop迴圈裡面,不過蔗不是本文重點
1 | int counter(void) { |
上面這個只是個玩具Coroutine,真正能拿來用的還分幾類
至於怎麼做就各顯神通了
- Implementing coroutines with ucontext
- Switching between coroutines/tasks: setjmp/longjmp (single stack)
- Coroutines in Assembler
Two difference model on Coroutine
就算是Coroutine,也可以分成兩類
- Stackful Coroutine
- Stackless Coroutine
顧名思義,差異就在對Stack的處理上面 - Stackless將State放在Heap上,而Stackful放在Stack上
- Stackless的大小是動態分配的,Stackful的Stack是固定大小的
- Stackless本質是個StateMachine,而Stackful是個User Mode Thread
因此Stackess Machine的Runtime消耗比較小,Stackful相反 - Stackful可以和舊有的synchronous code組合,Stackless不行
- Stackless需要Compilier支援,Stackful只需要Library就能做了
- Stackless的方案有傳染性,例如你在Javascrupt所看到的你的async/await是成雙成對的,布這麼用就會出錯,而Stackful沒有此限制
1
2
3async func1() {
await func2();
} - Stackful的程式好寫,Stackless需要一定能力
選邊站
由於兩種Model差異很大,由於程式語言的特性以及歷史因素,不同程式語言的選擇也不一樣
- Stackless:C#(第一個使用async/await的主流語言),Javascript,Python,C++,Rust,Kotlin(雖然是JVM的語言,不過跟Java選擇不同)
- Stackful:Golang(其實是變種的Coroutine),Java(照抄Golang那套,不過還沒推出),PHP(in the future)
Goroutine
前面提到,Goroutine是Stackful Coroutine的變形,最主要的差異在於
- coroutine是順序執行
- Goroutine可以在多個cpu平行執行的
因此又產生了分歧點
假設我們有Coroutine A,B,C
C等待B的資料,B等待A的資料 - 如果是傳統的Coroutine,A執行完會transfer到B,B執行完會transfer到C,由於在同一個CPU上,資料不用加鎖
- 如果是Goroutine,A,B,C三者可能在不同的CPU上跑,關於資料的傳遞只能透過Channel
- 由於Golang實作了一個有效利用Cpu Usage的Runtime,將corotuine定義成light weight thread,所以Golang Runtime需要做一部分OS需要做的事情,例如Schedule coroutine
- Mandatory goroutine,就算你寫一個hello world也避不掉
- Goroutine不快,Maximum network connection也比不上Stackless Coroutine(C++/Rust)
- 不過程式好寫太多,這強項才是goroutine搶走PHP/Python的主要原因
押錯寶
講講Rust押寶押錯的故事
IO Model有兩種
如同Coroutine有兩種,IO EventLoop也有兩種
- Proactor:最著名的就是Windows的IOCP了
- Reactor:select/poll/epoll等都是
Rust使用epoll的Reactor Model,不過epoll不是linux的未來
CPU Spectre and Meltdown
就跟COVID-19一樣,Spectre和Meltdown改變了寫程式的方向
因為CPU的Bug,Linux修正方向,io_uring才是Linux的未來,而io_uring和IOCP一樣,是Proactor的model
Influence
由於標準定了,要改改不了了
如果要改的話只有兩種選擇
- 重新制定標準,然後變成v2版本,光是制定一個版本花了四年,這次應該會快一點
- 兩個Model是可以互轉的,只是會有Performance Loss,當Spectre和Meltdown的Patch打上去之後會掉多少更難以估計
Conclusion
- 如果你是那95%的人,根本用不上Asynchronous programming,直接使用thread model,還不容易錯
- 如果不幸是那5%的人,首先考慮golang,golang就算幾千個缺點,goroutine都能掩蓋過去
golang適合寫網路服務,也只能寫網路服務 - 如果你是一秒鐘幾千萬上下,出來跑得遲早都要還,逃不掉C/C++/Rust寫code了
這裡有個實際案例
Why Discord is switching from Go to Rust - 沒有最好的方案,只有適合的方案

